FDDI and ATM both are part of the Network Operating System. Here in this article, You know about What is FDDI Network is, What is ATM with Explanation. Full-Form of FDDI, ATM.
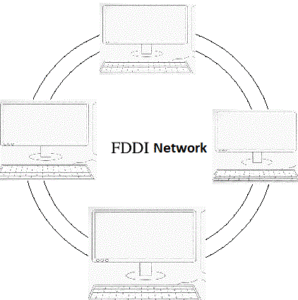
What is FDDI Network Explanation
- Full-Form of FDDI: Fiber Distributed Data Interface.
FDDI is a network protocol. Which is used primarily to interconnect two or more local area networks, often over large distances. The access method used by FDDI involves token-passing. FDDI uses a dual-ring physical topology. Transmission normally occurs on one of the rings; however, if a break occurs. So, the system keeps information moving by automatically using portions of the second ring to create a new complete ring. A major advantage of FDDI is Speed. It Operates over fiber optic cable at 100 Mbps.
Read Also: What is Topology in Computer Network
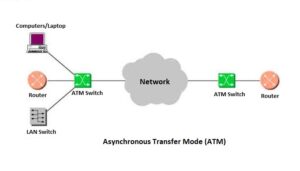
What is ATM Explanation
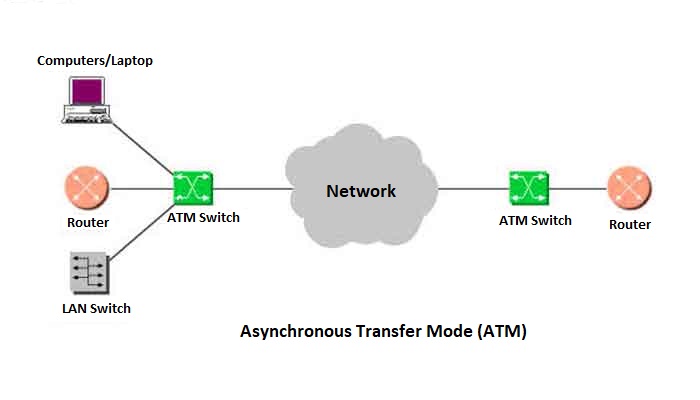
- Full-Form of ATM: Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
ATM is a network protocol that transmits data at a speed of 155 Mbps and higher. It’s working by transmitting all data in small packets of a fixed size; Whereas, other protocols transfer variable-length packets. Asynchronous Transfer Mode supports a variety of media such as video, CD-quality audio, and imaging. ATM employs a star topology, which can work with fiber optic as well as twisted pair cable.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode is most often used to interconnect two or more local area networks. It is also frequently used by Internet Service providers to utilize speed access to the Internet for their clients. However, as ATM technology becomes more cost-effective, it will provide another solution for constructing faster local area networks.
I hope, you get the information about FDDI and Asynchronous Transfer Mode(ATM). If you like this article, you can share and comment. So that we too have a chance to learn something from your ideas and improve something.
Read Also:
- List of Full Form Technologies and More
- What is Cache Memory in Computer, Mobile Phone
- Explain What is Kernel and Shell in UNIX